Mateusz BOGDAN
My personal site, with a short presentation of who I am, my academic and professional activities and research interests !
| Home |
|---|
| Research |
| Publications |
| Teachings |
| Datavisualisation |
| Code |
| Miscellanous |
Code snippets
Some useful tricks and hacks I use frequently, mostly in Python.
Python Basics
All my code snippets, my sort of personal cheet sheat, has been moved to this web site (in French), which I am developing as part of my teaching activities (work in progress). It is intended for students and covers Python fundamentals as well as practical dataframe tips.
Maps and GIS related questions
Recently I’ve ben working with maps in python applications. I mostly use geopandas, dash-leaflet, plotly.scattermapbox, etc.
Distance between two points on a sphere
Compute the distance in km (or meters) between 2 points of the globe defined by their respective lat / lon.
- It’s called a Haversine function.
- Basically, it’s trigonometry on a sphere !
- In the code snippet below
- If needed, you can adjust for the radius, with the last constant, which is
2*earth radius, in km, - To make thiong easy and work with degrees, everything is converted, hence the
p=0.017453292519943295value, which is actually a simplification, it should bep=Pi/180!def distance(lat1, lon1, lat2, lon2): # Haversine function to get distance in km from lat/lon points p = 0.017453292519943295 hav = 0.5 - cos((lat2-lat1)*p)/2 + cos(lat1*p) * \ cos(lat2*p) * (1-cos((lon2-lon1)*p)) / 2 # 2*6371.04 ~ 12742 (2*earth radius, in km) return 12742 * asin(sqrt(hav))
- If needed, you can adjust for the radius, with the last constant, which is
Moving on a sphere
- Starting from a point on an map defined by its latitude and longitude, what are the new cordinates if one moves, say 50m “to the right” (e.g. East), and 10m up (North) ? I’ve been strugling with that in pure python (some libraries probably do this type of calculation, but I wanted no dependancy). The solution I found comes from here.
It’s a function that allows you to compute exactly that: start from a point, move
xmeters in the “latitude” direction andymeters in the “longitude” direction, and compute the new coordinates:def translate_latlong(lat,long,lat_translation_meters,long_translation_meters): ''' method to move any lat,long point by provided meters in lat and long direction. params : lat,long: lattitude and longitude in degrees as decimal values, e.g. 37.43609517497065, -122.17226450150885 lat_translation_meters: movement of point in meters in lattitude direction. positive value: up move, negative value: down move long_translation_meters: movement of point in meters in longitude direction. positive value: left move, negative value: right move ''' earth_radius = 6378.137 #Calculate top, which is lat_translation_meters above m_lat = (1 / ((2 * np.pi / 360) * earth_radius)) / 1000; lat_new = lat + (lat_translation_meters * m_lat) #Calculate right, which is long_translation_meters right m_long = (1 / ((2 * np.pi / 360) * earth_radius)) / 1000; # 1 meter in degree long_new = long + (long_translation_meters * m_long) / np.cos(lat * (np.pi / 180)); return lat_new,long_new
Miscellaneous Functions
Daylength computation
What is the length of the day in hours ?
I needed to compute the length of days for a complete year, and I started using python libraries like pvlib with its module solarposition() or suntime to get the hours of sunset and sunrise. I kept looking for other solutions as I wanted to avoid dependancies, and i found a post on stackoverflow which gives you exactly that.
It is based on a paper by [Forsytthe et al., 1995], named A Model Comparison for Daylength as a Function of Latitude and Day of Year. It uses only the day_of_year and latitude and returns the length of the day in hours (and even have different definitions for the length of a day).
Usefully, one can provide a list of days of the year (or rather an np.array), and the function will return an array of the same length with daylengths :
- For a complete year calculation, I used
J = np.array([i for i in range(1,366)]).
def day_length(J, L):
"""
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Based upon : "A model comparison for daylength as a function of latitude and day of year"
Forsythe et al., 1995, Ecological Modelling 80 (1995) 87-95
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Parameters
----------
J: int / list of int / array
day of the year.
L: float
latitude (in °)
Returns
-------
Lenght of the day(s) in hours
To account for various definitions of daylength, modify the "p" value accordingly.
* Sunrise/Sunset is when the center of the sun is even with the horizon
p = 0
* Sunrise/Sunset is when the top of the sun is even with horizon
p = 0.26667
* Sunrise/Sunset is when the top of the sun is apparently even with horizon
p = 0.8333
"""
p = 0.8333
phi = np.arcsin(
0.39795 * ( np.cos( 0.2163108 + 2 * np.arctan( 0.9671396 * np.tan( 0.00860 * (J-186) ) ) ) )
)
D = 24 - (24/np.pi)*np.arccos(
( np.sin( p*np.pi/180 ) + np.sin( L*np.pi/180 ) * np.sin( phi ) ) / (np.cos(L*np.pi/180) * np.cos( phi ) )
)
return D
Web developments
I also contribute to bridging research and practice through web applications and digital tools.
- Development and maintenance of my team’s blog L’Hypercube, covering both front-end and back-end (Hugo, deployed on a cloud Ubuntu VM).
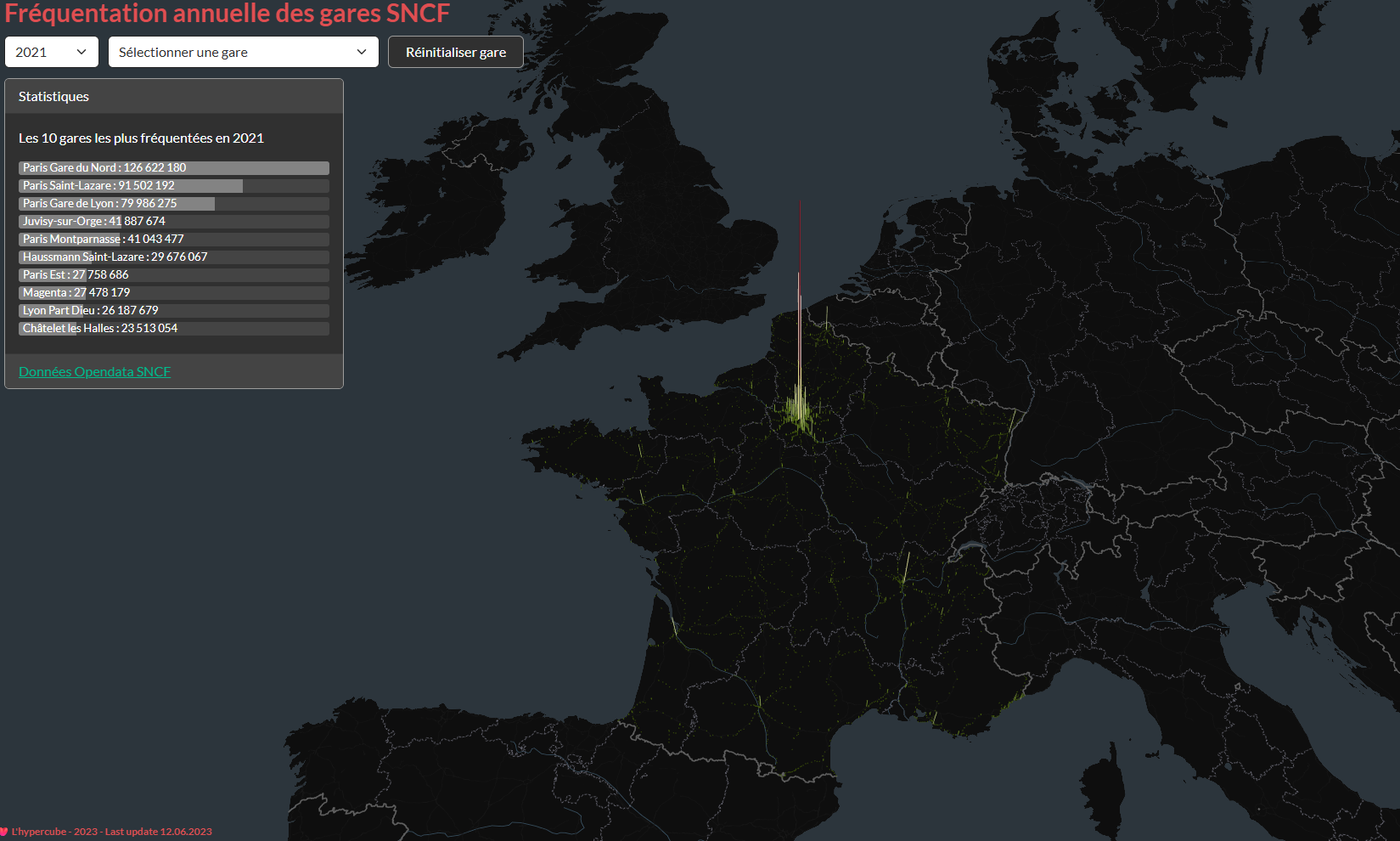
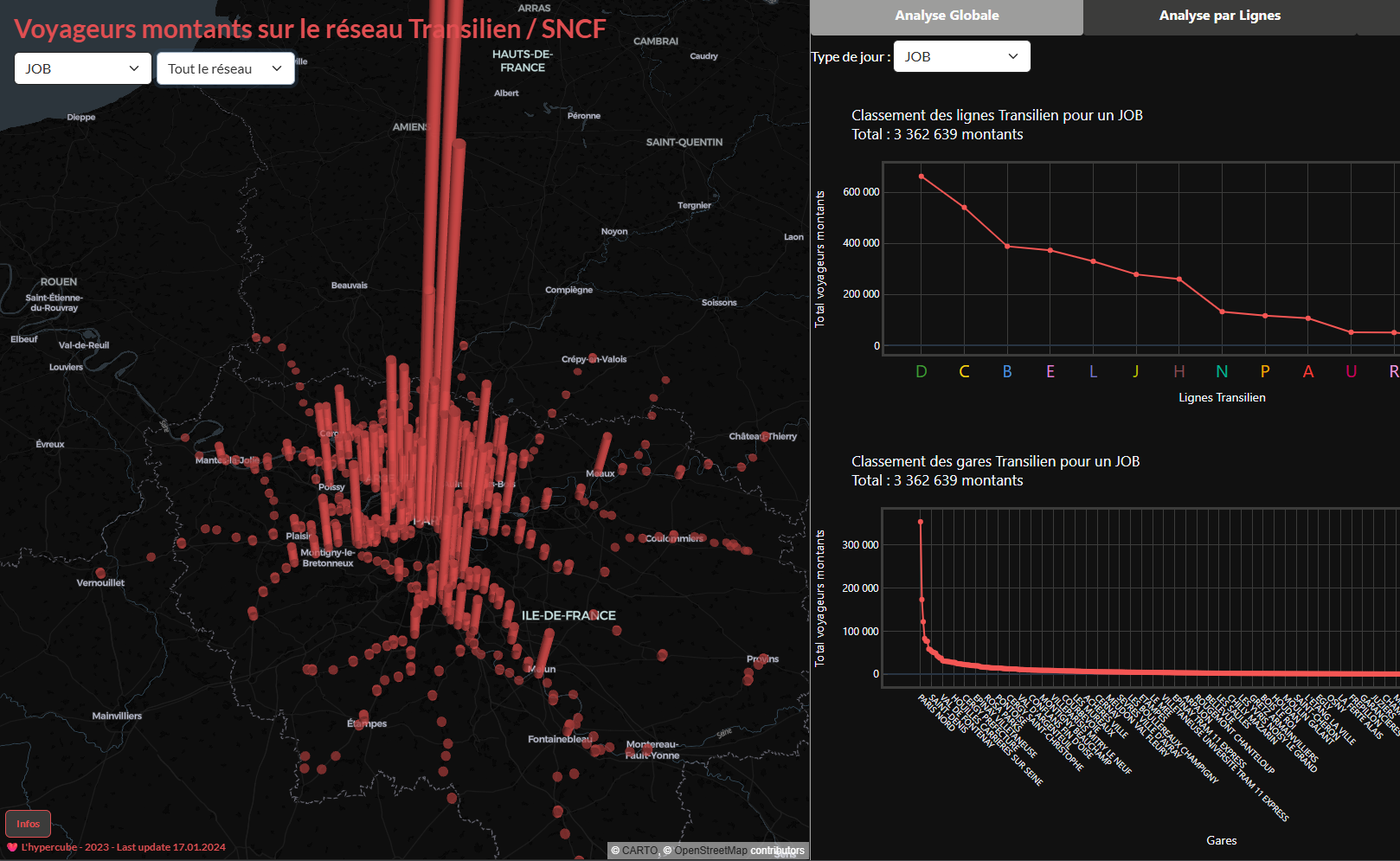
- Development of several dashboards with Dash, mainly internal to AREP, with some made publicly available on our website, often using SNCF open data: